X-ray
Radiographs, an important tool
Our hospital is fully equipped with the newest digital radiographic technology, to take radiographs (often called x-rays) of your pet. Our veterinarians will discuss your pet’s case and conduct a thorough physical examination to determine if your pet requires radiographs.
Radiographs are a very important tool to help us diagnose diseases in animals, particularly for conditions involving bones, the chest or abdomen.
What happens to my pet when it is booked in for radiographs?
Why do pets need to be sedated or anaesthetised to have radiographs taken?
When we have radiographs (x-rays) taken the radiographer asks us to keep perfectly still, often in unnatural positions. Most pets would never lie still enough, in the correct position, for us to take good quality radiographs required to diagnose their condition. Sedation and anaesthesia allow us to get the most useful radiographs possible.
How are radiographs made?
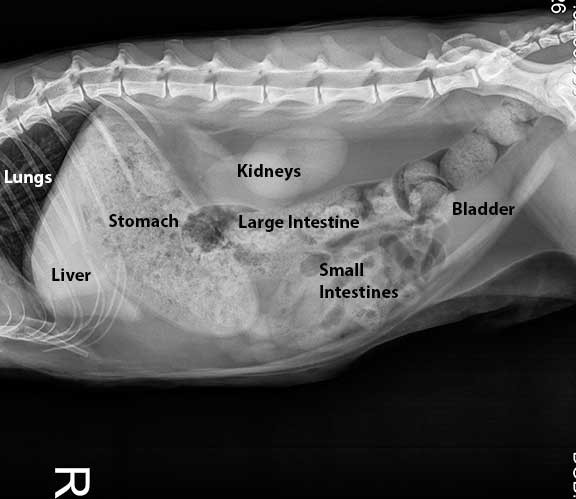
Different tissues in the body absorb x-rays to differing degrees. Of all the tissues in the body, bone absorbs the most x-rays. This is the reason that bone appears white on a radiograph.
Soft tissues, such as lungs or organs, absorb less of the x-rays, so soft tissues appear on a radiograph in different shades of grey.
